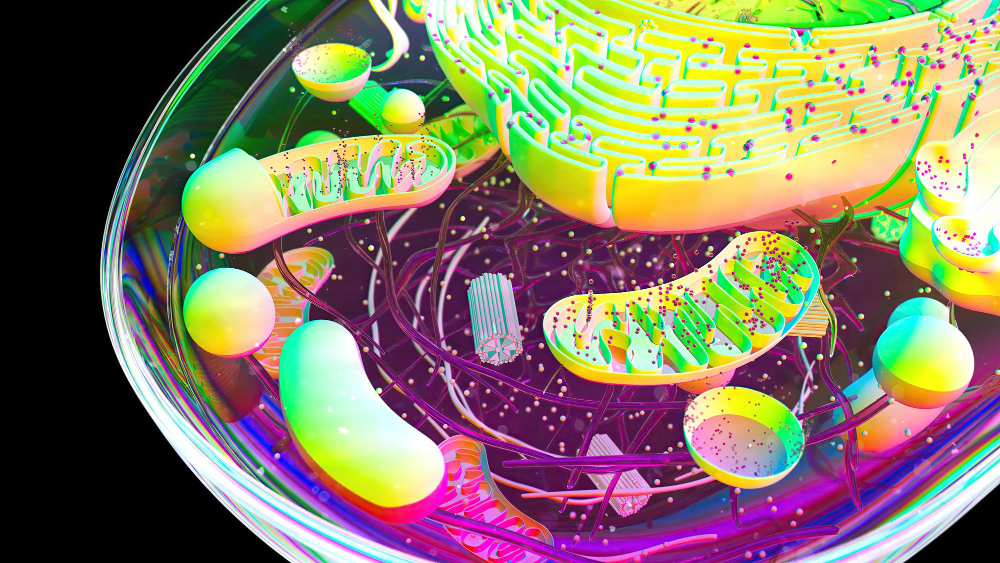
What Structure Controls the Cell’s Activities
Within the intricate world of biology, the cell stands as the fundamental unit of life, a bustling microcosm of activity governed by a complex interplay of structures and processes. At the heart of this bustling hub lies a crucial structure that orchestrates the cell’s activities, dictating everything from growth and reproduction to metabolism and response to external stimuli. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of cellular biology and uncover the structure that holds the reins of cellular function.
Keeper of the Genetic Blueprint
Situated at the core of eukaryotic cells, the nucleus serves as the command center, housing the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). Within the nucleus, DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes, which contain the instructions for synthesizing proteins and carrying out cellular processes. The nucleus plays a pivotal role in regulating gene expression, controlling which genes are turned on or off in response to internal and external cues, thereby influencing the cell’s activities.
Highway of Cellular Communication
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a vast network of membrane-bound tubules and sacs that extends throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Divided into rough and smooth regions, the ER plays multiple roles in cellular function. The rough ER is studded with ribosomes, where protein synthesis occurs, while the smooth ER is involved in lipid metabolism, detoxification, and calcium storage. This intricate network serves as a highway for communication and transport within the cell, facilitating the movement of proteins and other molecules to their designated destinations.
Powerhouses of the Cell
Renowned as the powerhouses of the cell, mitochondria are double-membraned organelles responsible for generating adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell. Through a process called cellular respiration, mitochondria harness the energy stored in nutrients to produce ATP, fueling cellular activities ranging from metabolism to cell division. Additionally, mitochondria play a role in regulating apoptosis, or programmed cell death, and contribute to calcium homeostasis within the cell.
The Cell’s Post Office
Named after Italian biologist Camillo Golgi, the Golgi apparatus is a membranous organelle involved in processing, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other cellular compartments. Acting as the cell’s post office, the Golgi apparatus modifies proteins and lipids synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum, adding molecular tags that direct them to their intended destinations. This complex organelle plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring the proper functioning of the secretory pathway.
Structural Support and Dynamic Mobility
Comprising a network of protein filaments, the cytoskeleton provides structural support, maintains cell shape, and facilitates cellular movement and transport. Consisting of three main components—microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules—the cytoskeleton acts as a dynamic scaffold, orchestrating various cellular processes such as cell division, intracellular transport, and cell motility. Through interactions with molecular motors and regulatory proteins, the cytoskeleton enables cells to respond to mechanical cues and navigate their environment with precision.
Gatekeeper of Cellular Communication
Surrounding the cell like a delicate membrane, the plasma membrane serves as a selective barrier, regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the cell. Composed of a lipid bilayer embedded with proteins, the plasma membrane plays a vital role in cellular communication, signaling, and recognition. Through the integration of receptor proteins and ion channels, the plasma membrane enables cells to sense and respond to changes in their environment, ensuring their survival and adaptation to diverse conditions.
A Symphony of Structures
As we unravel the mysteries of cellular biology, it becomes clear that the cell’s activities are governed by a symphony of structures working in harmony. From the nucleus, where the genetic blueprint resides, to the mitochondria, which power cellular function, each organelle plays a unique yet interconnected role in orchestrating the intricate dance of life. By understanding the structure and function of these cellular components, scientists can unlock the secrets of health and disease, paving the way for innovative therapies and treatments that harness the power of the cell.


